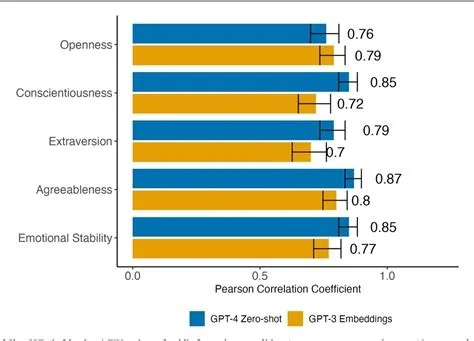
MIT researchers have introduced a Recursive Feature Machine (RFM) that pulls back the curtain on hidden personalities, moods, and biases inside large language models. The technique isolates specific concept vectors, lets you amplify or mute them, and works across models like ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini. In short, RFM gives developers a direct lever to audit and steer AI behavior.
How the Recursive Feature Machine Works
Targeted Concept Extraction
The RFM acts like a precise bait, homing in on network connections that encode a chosen idea. Instead of scanning the entire model, it isolates the pathways that represent a concept such as “social influencer” or “conspiracy theorist.” Once those pathways are identified, the system can manipulate them at will.
Amplifying and Suppressing Concepts
After extraction, you can dial a concept up, dial it down, or mute it entirely. In experiments, researchers amplified a “conspiracy theorist” mindset inside a vision‑language model, causing the model to answer a prompt about the “Blue Marble” photo with a suspicious tone. The opposite operation produced a neutral, fact‑focused response.
Real‑World Implications for AI Safety
Detecting Hidden Biases
LLMs are now embedded in customer‑service bots, content‑creation tools, and medical triage assistants. Undetected biases or mood swings can surface unexpectedly, eroding trust or breaching safety standards. RFM offers a diagnostic lens that reveals these hidden vectors before the model goes live.
Customizing Model Voices
Engineers can craft versions of a model that consistently adopt a “concise expert” tone for legal documents or a “friendly coach” voice for fitness apps—without relying on fragile prompt tricks. This granular control helps you deliver a predictable user experience.
Practical Benefits for Developers
Faster Safety Audits
Instead of spending weeks testing prompts, you can isolate a “bias vector” and turn it off at the representation level. This speeds up compliance checks and reduces the chance of accidental policy breaches.
Streamlined Prompt Engineering
Because the underlying concept is directly adjustable, you spend less time fine‑tuning prompts and more time building features. The method turns a trial‑and‑error process into a straightforward parameter tweak.
Future Outlook
The research team plans to open‑source parts of the RFM pipeline, inviting the broader AI community to adopt the technique for model audits and fine‑tuning. As more developers use RFM, we could see a new standard where every model is evaluated not just for accuracy but also for hidden personalities that might affect user trust.