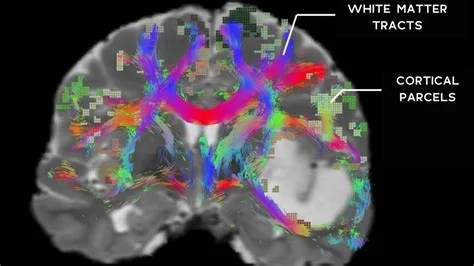
MIT’s new BrainStem Bundle Tool (BSBT) lets you automatically map eight critical white‑matter pathways in the brainstem from any diffusion‑MRI scan in just seconds. Powered by deep‑learning, the open‑source algorithm eliminates the tedious manual tracing that has limited brainstem research for years. Clinicians can now get a quantitative read‑out of brainstem health, speeding diagnosis and treatment monitoring.
How the BrainStem Bundle Tool Works
BSBT uses a convolutional neural network trained on expertly labeled scans to recognize the medial longitudinal fasciculus, dorsal longitudinal fasciculus, and six other bundles. Once the model sees a diffusion‑MRI volume, it instantly produces a full‑brainstem segmentation without any user input.
Key Features and Speed
- Automatic segmentation of eight brainstem pathways
- Runs in seconds on standard workstation hardware
- Open‑source code enables easy integration into existing pipelines
Clinical Impact Across Neurological Disorders
When researchers applied BSBT to patients with Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, traumatic brain injury, and Alzheimer’s disease, distinct patterns of white‑matter alteration emerged for each condition. In one striking case, the tool tracked the gradual restoration of brainstem pathways in a patient emerging from a seven‑month coma, mirroring the clinical recovery timeline.
What This Means for You as a Clinician
With a quantitative read‑out of brainstem integrity, you can detect neurodegenerative changes earlier and monitor treatment response with unprecedented precision. The algorithm also highlights subtle respiratory or cardiovascular control disruptions that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Research Opportunities and Future Directions
Beyond the clinic, BSBT gives basic scientists a reliable map to explore long‑standing questions about consciousness, arousal, and autonomic regulation. The team plans to expand the toolbox to cover additional subcortical structures and to validate the method in prospective clinical trials.
Practical Integration in Hospital Pipelines
Because the software is open‑source, hospitals can embed it directly into their imaging workflows without waiting for commercial vendors. This reduces bottlenecks, cuts processing time from hours to minutes, and makes large‑scale studies feasible.